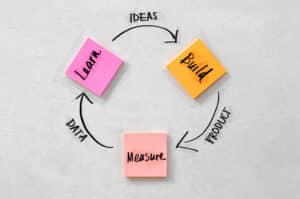
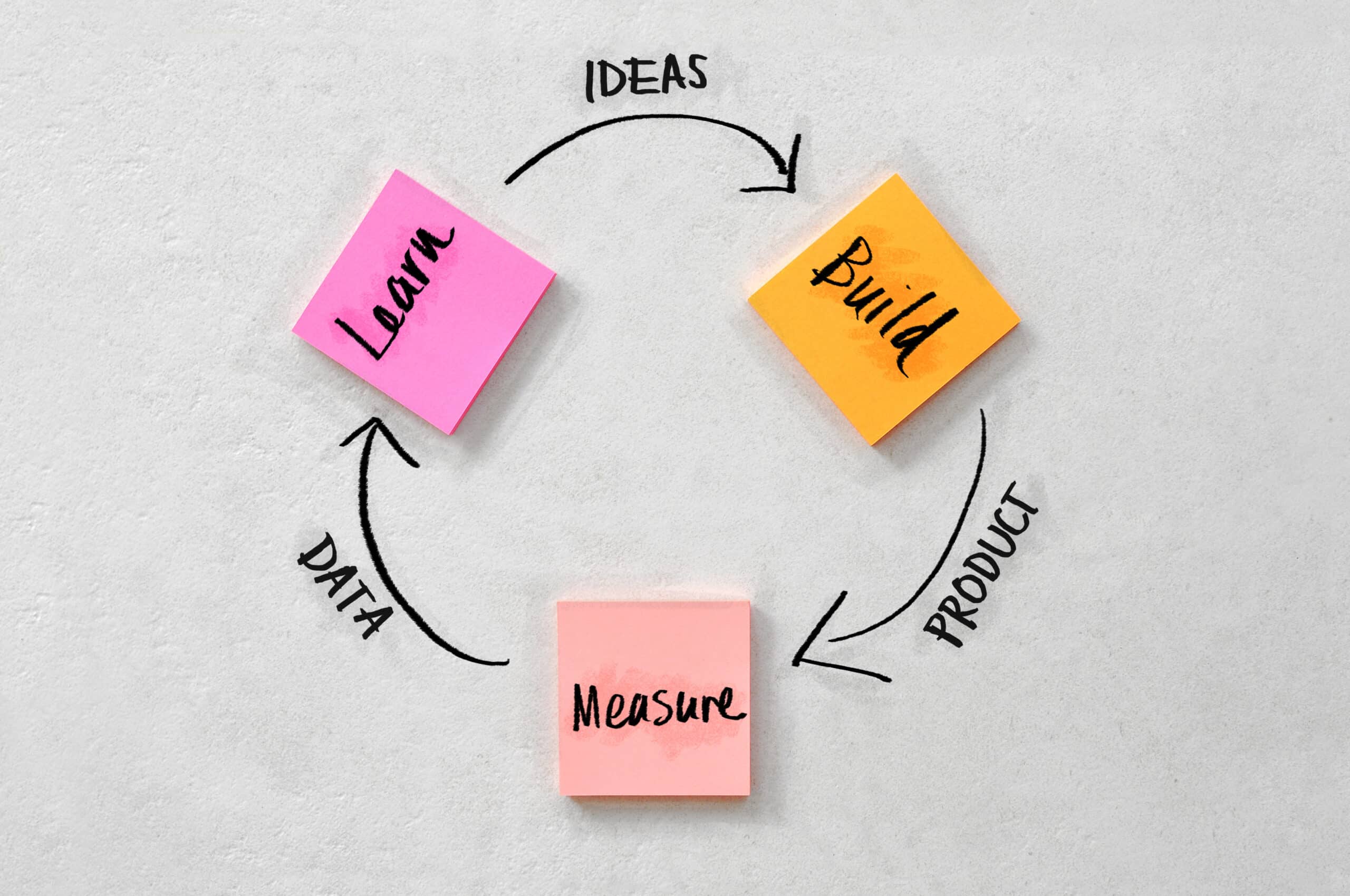
Establishing your business’ terms and conditions may seem like an arduous task among the never-ending to-do lists. Getting your business’ terms and conditions right is essential for healthy cash flow.
The terms and conditions form the basis for the trading relationship on which a business sells goods and services to customers and buys goods and services from suppliers. Terms and conditions can be the difference between chasing up late payments to ensuring that your business is paid first.
Well-drafted terms and conditions will protect a business and clarify what should happen in any given situation. Terms and conditions can also prevent disputes and save time and money on collecting debts.
While there is no legal requirement to include terms and conditions on invoices, a Business should establish written terms and conditions to protect itself if things go wrong with one party. The terms and conditions you decide to incorporate will vary depending on your business’ needs but generally should include:
Goods and services
A clear definition of the goods and/or services that will be provided. Including a section for definitions of the words used throughout your terms and conditions will prevent any misunderstandings or misinterpretation.
Price and Payment Terms
The price should be defined and must state whether GST (or other taxes) are included or not. The payment terms should outline when the payment is due and if the price is payable in cash on delivery or pre-agreed terms.
Warranties Or Guarantees
Include any warranty that will be provided. Business terms need to clearly explain the warranty period and limitations under warranty. If you offer any guarantees, be sure to include them and remember guarantees should be provided before any goods and services are provided.
Delivery
A Business should have a timeline for the delivery of goods. Ensure to include the method of delivery and any associated costs for delivery.
Credit
If credit is provided, make sure to include the credit terms, credit limit and any penalty or default terms. It is essential to request permission to conduct a reference check to check the other party’s creditworthiness before providing credit. Businesses offering credit increases the chances of receiving a late payment. A business may not even receive payment. A business should then consider upfront payment or payment on delivery.
Risk
Specify what will happen if either party does not deliver or pay on time. The terms should also state what notice is required to get out of an agreement or if one party wants to end the relationship.
Retention of Title Clause
The retention of title (ROT) clause means that the seller can retain the ownership of goods already supplied until the other party has paid for them. Suppliers must ensure to register their interest in accordance with the Personal Property Security Act to remain enforceable.